Artificial intelligence and humans: competition or cooperation?
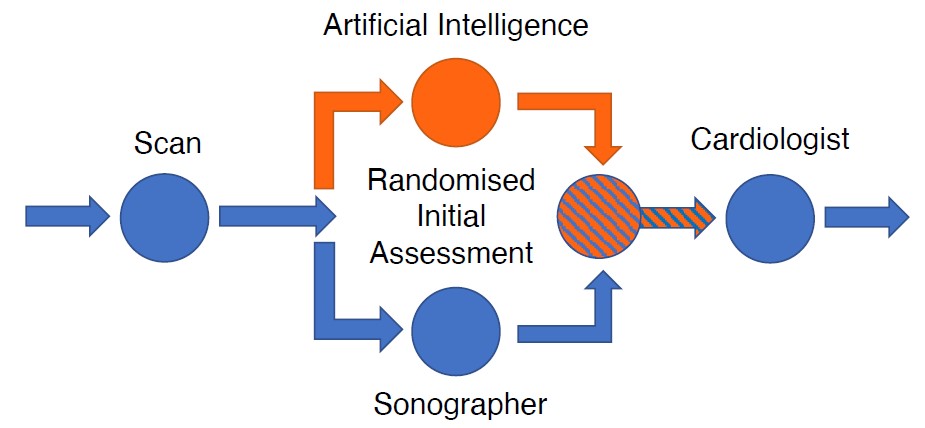
Even though there is much noise regarding the role of AI tools in healthcare, data from prospective, well-designed clinicaltrials are lacking. It is known that LVEF is essential for the diagnosis and therapy of many diseases. Sonographers usually base their decision on the assessment of a limited number of echo frames. Echo-Net Dynamic is a deeplearning algorithm trained to accurately assess cardiac function by echo videos developed by researchers from Stanford University, and the Cedars-Sinai Medical Center. The EchoNet-RCT is a blinded, randomized controlled study designed to study if AI guided measurements of left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) can save time and improve accuracy of echo assessment. In this trial the echo scans were randomly allocated 1:1 to AI initial assessment or sonographer initial assessment. The study included 3,495 transthoracic echocardiograms performed on adults. The results of the EchoNet-RCT presented in a Hot Line session at ESCCongress 2022 in Barcelona, demonstrated that scans assessed by the AI tool were significantly closer to the final cardiologist report, compared to those read by a sonographer. How will this affect the future? Dr. David Ouyang the PI of the trial mentioned AI will help and support doctors to improve their diagnostic capabilities, rather than stealing their jobs.
Find the ESC press release here. Find the ESC EchoNet-RCT study results presentation here.
Find the originalarticle for the Echo-Net Dynamic here.


